


What is Plastic Injectiong Moudling Process?
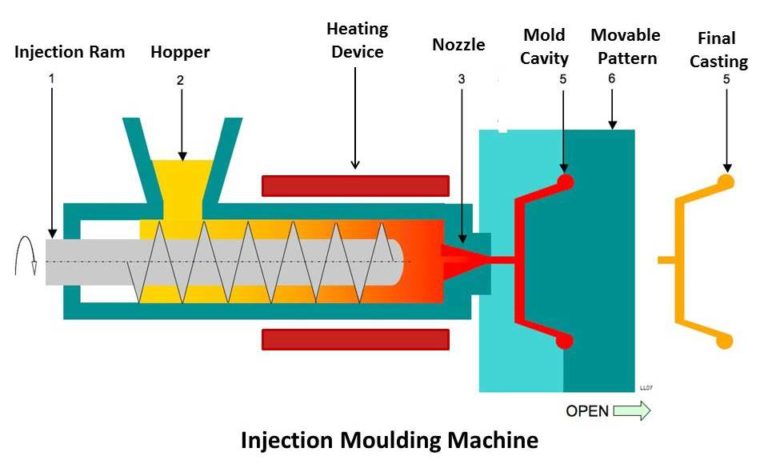
Injection moulding is a manufacturing process for producing parts by injecting molten material into a mould or mold. Injection moulding can be performed with a host of materials mainly including metals (for which the process is called die-casting), glasses, elastomers, confections, and most commonly thermoplastic and thermosetting polymers. Material for the part is fed into a heated barrel, mixed (using a helical screw), and injected into a mould cavity, where it cools and hardens to the configuration of the cavity, After a product is designed, usually by an industrial designer or an engineer, moulds are made by a mould-maker (or toolmaker) from metal, usually either steel or aluminium, and precision-machined to form the features of the desired part. Injection moulding is widely used for manufacturing a variety of parts, from the smallest components to entire body panels of cars. Advances in 3D printing technology, using photopolymers that do not melt during the injection moulding of some lower-temperature thermoplastics, can be used for some simple injection moulds.


Material
Mold Temperature(°C)
Melt Temperature(°C)
Melt Pressure(MPa)
PE
60-70
170-200
60-100
PP
80-90
160-220
70-100
PC
60-110
230-285
80-130
POM
90-120
160-190
80-130
ABS
50-80
170-200
60-100
PMMA
40-60
160-180
80-130
Surface Finish Options
Draft angle requirements will vary by requested finish. Industry standard Mold-Tech finishes are also available. 
FINISH
DESCRIPTION
PM-F0
non-cosmetic, finish to Protolabs' discretion
PM-F1
low-cosmetic, most toolmarks removed
PM-F2
non-cosmetic, EDM permissible
SPI-C1
600 grit stone, 10-12 Ra
PM-T1
SPI-C1 + light bead blast
PM-T2
SPI-C1 + medium bead blast
SPI-B1
600 grit paper, 2-3 Ra
SPI-A2
grade #2 diamond buff, 1-2 Ra
What's main defect of injection molding?
The complexity of the injection molding process, and the interdependence of the many variables involved, means that any molding defect may have several different causes, of which more than one may be present at any given time
| Problem |
Possible Causes |
Picture |
| Sink Marks |
Melt temperature too high
Insufficient material injected
Insufficient dwell time
Premature gate freezing
Sharp variations in wall thickness
Wrong gate location
Part ejected too hot
Cavity pressure too low
|
 |
| Voids |
Volatiles from overheated material
Condensation on granules
Premature freezing of flow path to thick section
|
 |
|
Flow marks
|
Melt temperature too low |
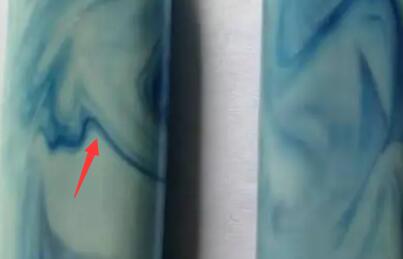 |
|
Weld lines |
Incorrect gate location mold temperature too low |
 |
|
Burn marks |
Incorrect filling pattern |
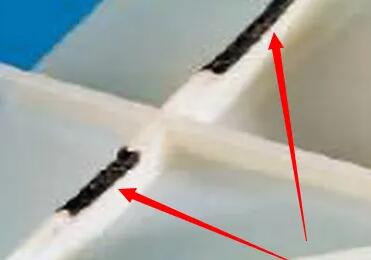 |
|
Warping |
Melt temperature too low
Incorrect part design
Overpacking near gate
Sharp variations in wall thickness
Flow length too great
Unbalanced multiple gates
Part ejected too hot
Inadequate or badly located ejectors
Temperature variations between the mold halves
|
 |
|
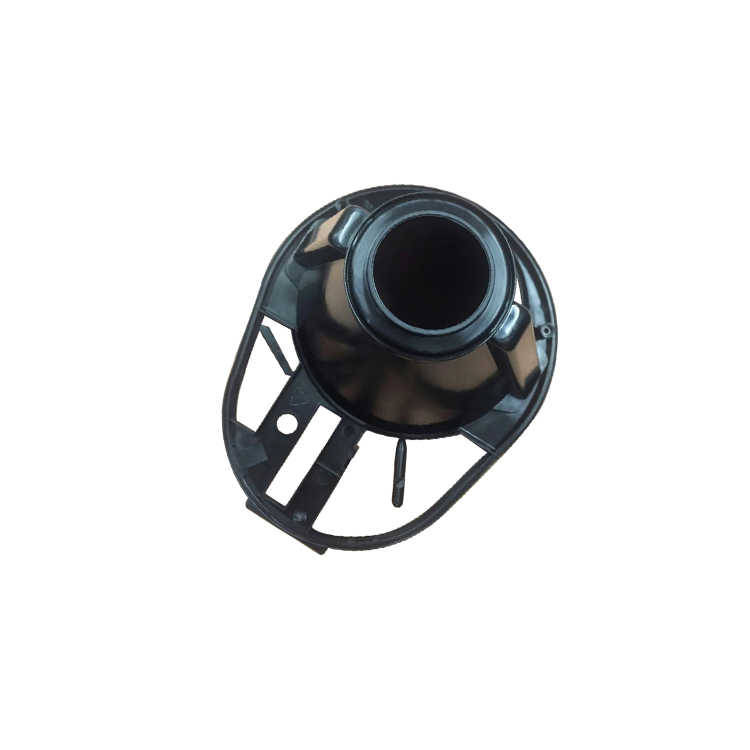
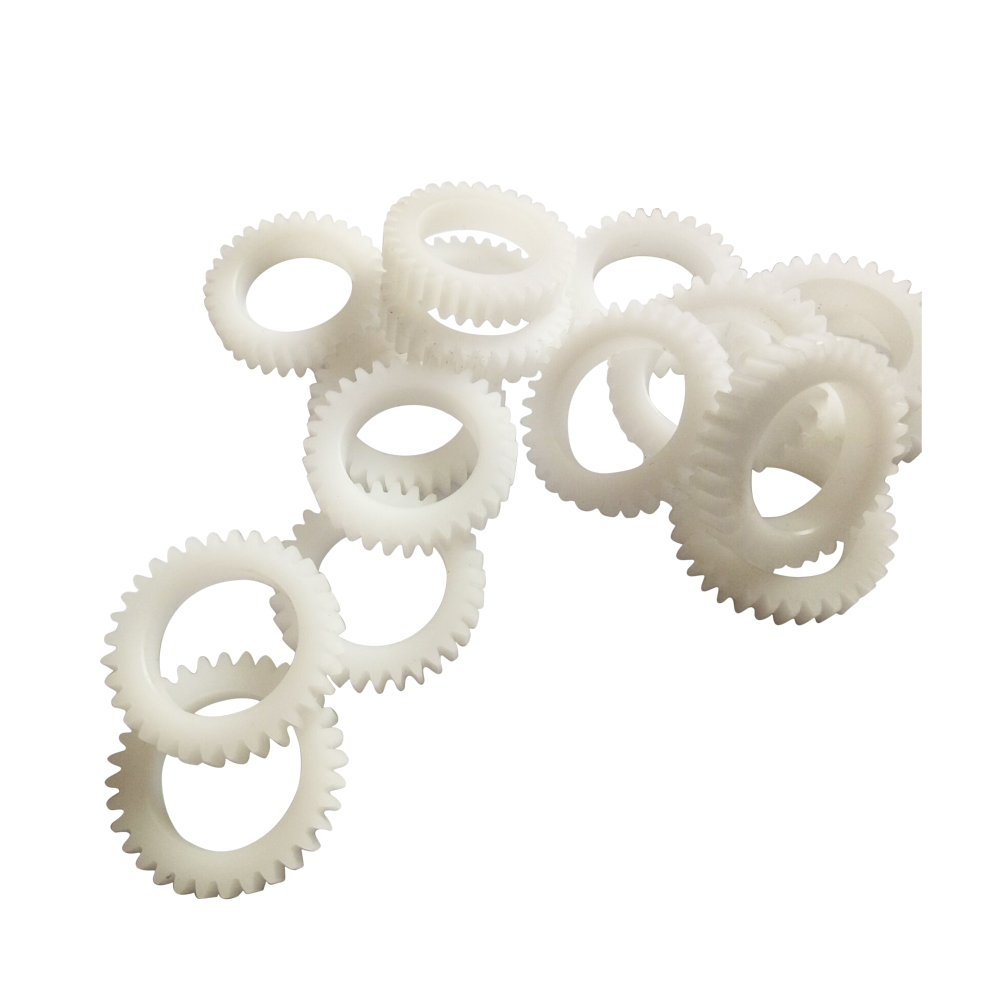
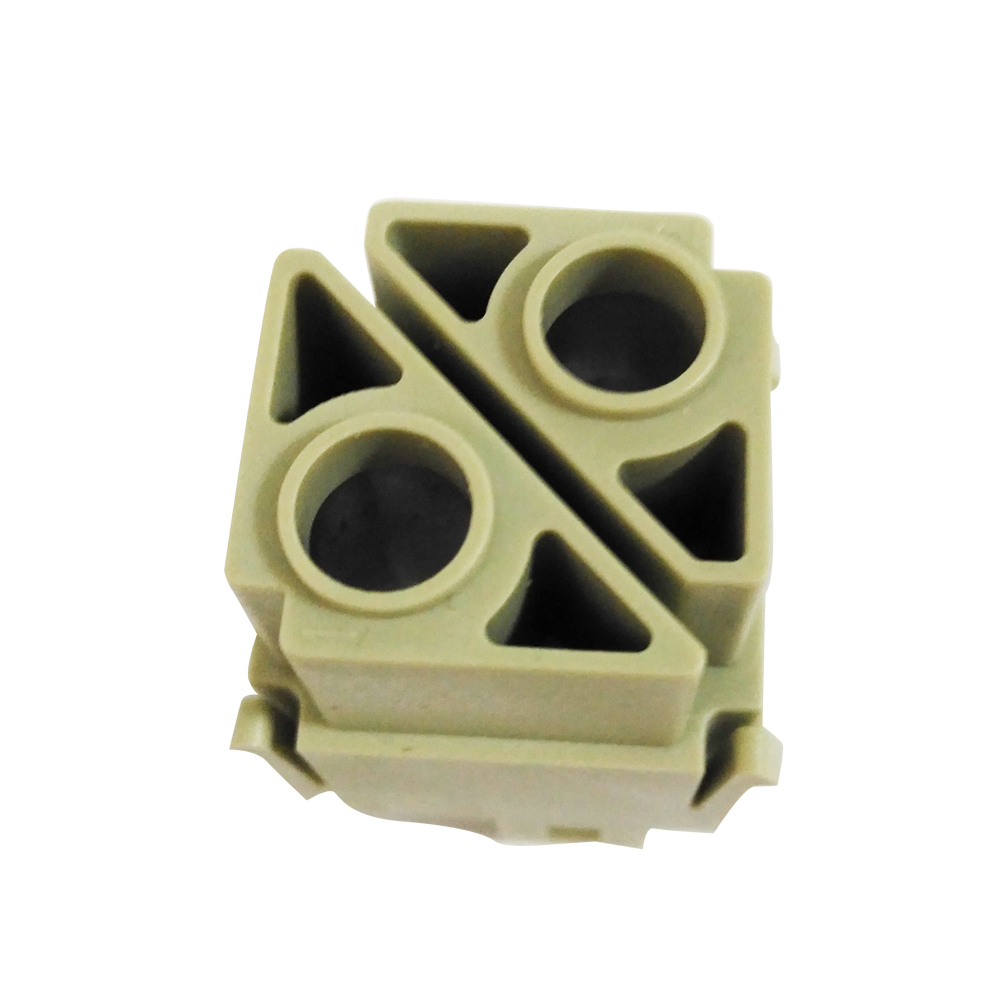
Some Case From Xiamen wiesel Technology co.,Ltd |
|||
 |
 |
 |
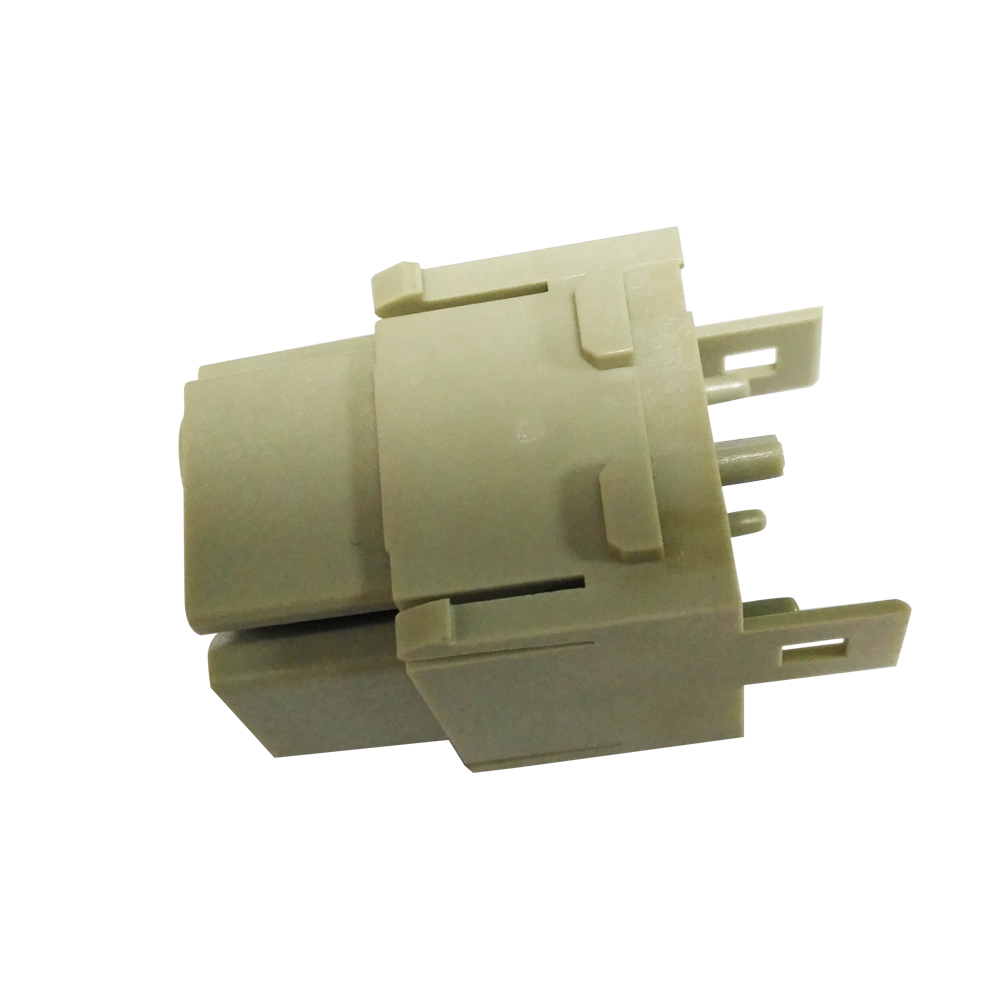 |
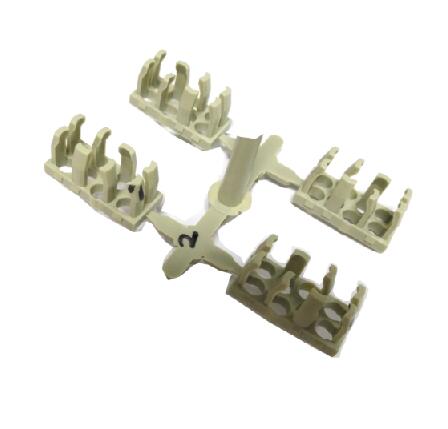 |
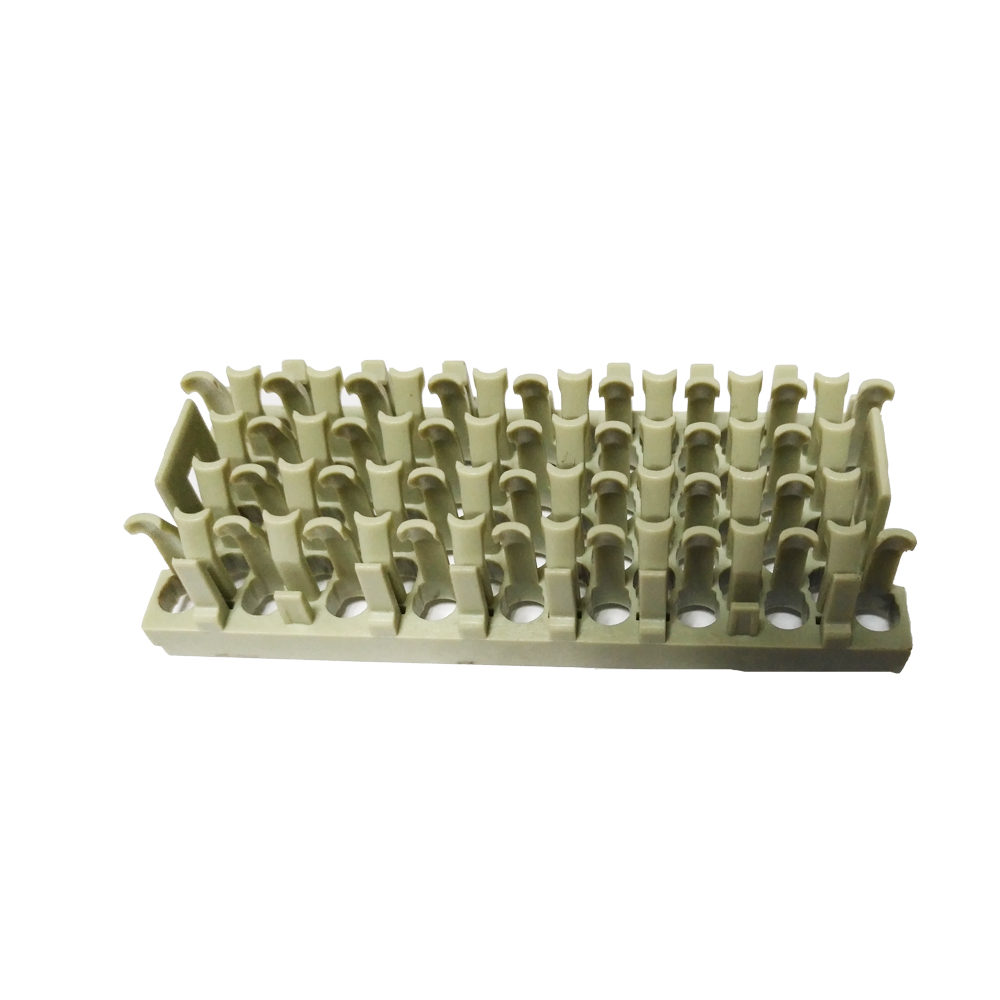 |
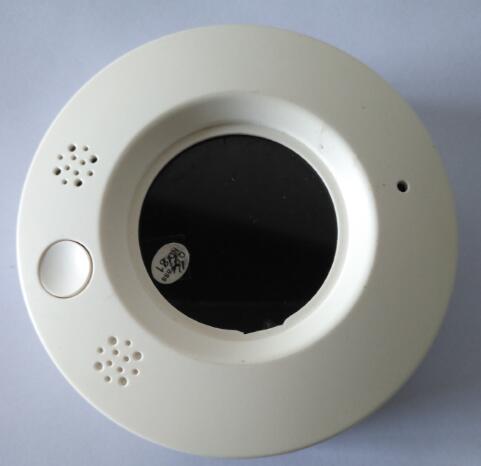 |
 |